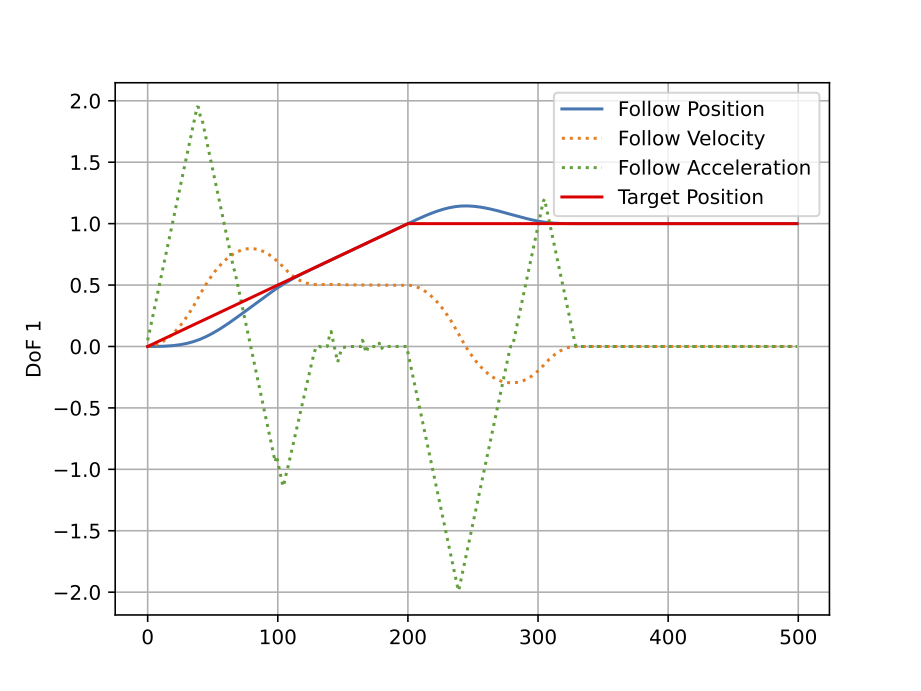
Example 14: Tracking of arbitrary signals with Velocity, Acceleration, and Jerk Limits
C++
// Only with Ruckig Pro
#include <cmath>
#include <ruckig/trackig.hpp>
#include "plotter.hpp"
using namespace ruckig;
// Create the target state signal
TargetState<1> target;
const bool on_ramp = t < ramp_pos / std::abs(ramp_vel);
target.position[0] = on_ramp ? t * ramp_vel : ramp_pos;
target.velocity[0] = on_ramp ? ramp_vel : 0.0;
target.acceleration[0] = 0.0;
return target;
}
TargetState<1> target;
target.position[0] = t * t * ramp_acc;
target.velocity[0] = t * ramp_acc;
target.acceleration[0] = ramp_acc;
return target;
}
TargetState<1> target;
target.position[0] = std::sin(ramp_vel * t);
target.velocity[0] = ramp_vel * std::cos(ramp_vel * t);
target.acceleration[0] = -ramp_vel * ramp_vel * std::sin(ramp_vel * t);
return target;
}
int main() {
// Create instances: the Trackig trajectory generator as well as input and output parameters
Trackig<1> trackig(0.01); // control cycle
InputParameter<1> input;
OutputParameter<1> output;
// Set input parameters
input.current_position = {0.0};
input.current_velocity = {0.0};
input.current_acceleration = {0.0};
input.max_velocity = {0.8};
input.max_acceleration = {2.0};
input.max_jerk = {5.0};
// Optional minimum and maximum position
input.min_position = {-2.5};
input.max_position = {2.5};
trackig.mode = TrackigMode::Optimized; // Optimized or Fast
trackig.reactiveness = 1.0; // default value, should be in [0, 1]
// Generate the trajectory following the target state
std::cout << "target | follow" << std::endl;
for (size_t t = 0; t < 500; t += 1) {
const Result res = trackig.update(target_state, input, output);
std::cout << pretty_print(target_state.position) << " | " << pretty_print(output.new_position) << std::endl;
output.pass_to_input(input);
}
}
TargetState< 1 > model_constant_acceleration(double t, double ramp_acc=0.05)
Definition 14_tracking.cpp:22
TargetState< 1 > model_ramp(double t, double ramp_vel=0.5, double ramp_pos=1.0)
Definition 14_tracking.cpp:13
CustomVector< double, DOFs > current_acceleration
Definition input_parameter.hpp:190
CustomVector< double, DOFs > current_velocity
Definition input_parameter.hpp:190
CustomVector< double, DOFs > max_velocity
Velocity limit.
Definition input_parameter.hpp:196
CustomVector< double, DOFs > current_position
Current (start) state.
Definition input_parameter.hpp:190
CustomVector< double, DOFs > max_jerk
Jerk limit.
Definition input_parameter.hpp:202
std::optional< CustomVector< double, DOFs > > min_position
Minimum positional limit (only in Ruckig Pro)
Definition input_parameter.hpp:222
std::optional< CustomVector< double, DOFs > > max_position
Maximum positional limit (only in Ruckig Pro)
Definition input_parameter.hpp:219
CustomVector< double, DOFs > max_acceleration
Acceleration limit.
Definition input_parameter.hpp:199
CustomVector< double, DOFs > new_position
New position values at the given time.
Definition output_parameter.hpp:38
void pass_to_input(InputParameter< DOFs, CustomVector > &input) const
Copies the new output state to the current state of the input.
Definition output_parameter.hpp:129
Definition block.hpp:16
Result
Result type of methods calculating trajectories (e.g. Ruckig's and Trackig's update and calculate)
Definition result.hpp:7
std::string pretty_print(const Vector &array)
Join a vector for pretty printing (e.g. to std::cout)
Definition plotter.hpp:11
Python
# Only with Ruckig Pro
from math import sin, cos
from ruckig import Trackig, TrackigMode, TargetState, InputParameter, OutputParameter
# Create the target state signal
def model_ramp(t, ramp_vel=0.5, ramp_pos=1.0):
target = TargetState(1)
on_ramp = t < ramp_pos / abs(ramp_vel)
target.position = [t * ramp_vel] if on_ramp else [ramp_pos]
target.velocity = [ramp_vel] if on_ramp else [0.0]
target.acceleration = [0.0]
return target
def model_constant_acceleration(t, ramp_acc=0.05):
target = TargetState(1)
target.position = [t * t * ramp_acc]
target.velocity = [t * ramp_acc]
target.acceleration = [ramp_acc]
return target
def model_sinus(t, ramp_vel=0.4):
target = TargetState(1)
target.position = [sin(ramp_vel * t)]
target.velocity = [ramp_vel * cos(ramp_vel * t)]
target.acceleration = [-ramp_vel * ramp_vel * sin(ramp_vel * t)]
return target
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create instances: the Trackig OTG as well as input and output parameters
inp = InputParameter(1)
out = OutputParameter(inp.degrees_of_freedom)
otg = Trackig(inp.degrees_of_freedom, 0.01)
# Set input parameters
inp.current_position = [0.0]
inp.current_velocity = [0.0]
inp.current_acceleration = [0.0]
inp.max_velocity = [0.8]
inp.max_acceleration = [2.0]
inp.max_jerk = [5.0]
# Optional minimum and maximum position
inp.min_position = [-2.5]
inp.max_position = [2.5]
otg.mode = TrackigMode.Optimized # Optimized or Fast
otg.reactiveness = 1.0 # default value, should be in [0, 1]
print('target | follow')
# Generate the trajectory following the target state
steps, target_list, follow_list = [], [], []
for t in range(500):
target_state = model_ramp(otg.delta_time * t)
steps.append(t)
res = otg.update(target_state, inp, out)
out.pass_to_input(inp)
print(
'\t'.join([f'{p:0.3f}' for p in target_state.position] + [f'{p:0.3f}' for p in out.new_position]),
f'in {out.calculation_duration:0.2f} [µs]',
)
target_list.append([target_state.position, target_state.velocity, target_state.acceleration])
follow_list.append([out.new_position, out.new_velocity, out.new_acceleration])
# Plot the trajectory
# from pathlib import Path
# project_path = Path(__file__).parent.parent.absolute()
# import numpy as np
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# follow_list = np.array(follow_list)
# target_list = np.array(target_list)
# plt.ylabel(f'DoF 1')
# plt.plot(steps, follow_list[:, 0], label='Follow Position')
# plt.plot(steps, follow_list[:, 1], label='Follow Velocity', linestyle='dotted')
# plt.plot(steps, follow_list[:, 2], label='Follow Acceleration', linestyle='dotted')
# plt.plot(steps, target_list[:, 0], color='r', label='Target Position')
# plt.grid(True)
# plt.legend()
# plt.savefig(project_path / 'examples' / '13_trajectory.pdf')
Output Trajectory